SSC CGL 2017: New Syllabus and Exam Pattern
It is very important for the aspiring candidates to have complete knowledge of SSC CGL 2017 syllabus & exam pattern, so that they can prepare a better and neat time table by covering all the topics as per official syllabus and new pattern. Candidates are advised to prepare strictly according to new exam pattern & selection scheme to crack upcoming SSC CGL 2017 Exam.
Changes in SSC CGL Exam Pattern 2017
- Now SSC will conduct both Tier -I and Tier II exam in online mode.
- Introduce a descriptive paper of 100 marks within 60 minutes in pen and paper mode.
- Reduce the time limit for examination of Tier -I from 120 minutes to 75 minutes.
- Tier II will remain same.
- No Sectional Cut off.
The Examination will be conducted in four tiers as indicated below:
Tier -I -- Written Examination (Objective Multiple Choice Type)
Tier -II -- Written Examination (Objective Multiple Choice Type)
Tier -III --Descriptive Paper in English/Hindi (writing of Essay/Precis/Letter /Application Writing
Tier -IV -- Computer Proficiency Test/ Skill Test (wherever applicable)/ Document Verification
SSC CGL 2017 Detailed New Syllabus 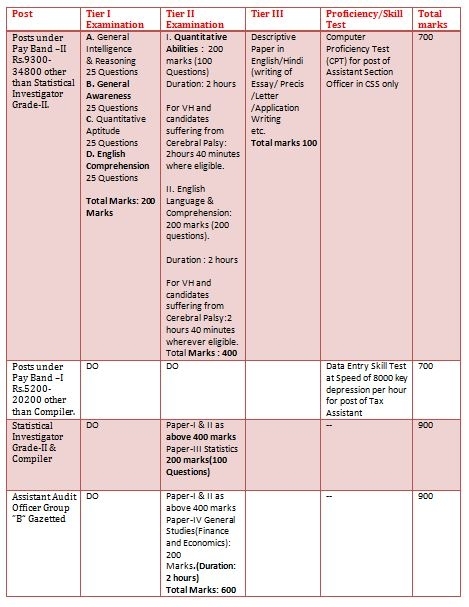 Combined Graduate Level (Tier-I) Exam 2017: Big Changes
Combined Graduate Level (Tier-I) Exam 2017: Big Changes
General Intelligence & Reasoning
This component may include questions on: -
(i) analogies, similarities and differences, space visualization, spatial orientation, problem solving, analysis, judgment, decision making, visual memory, discrimination, observation, relationship concepts, arithmetical reasoning and figural classification, arithmetic number series, non-verbal series, coding and decoding, statement conclusion, syllogistic reasoning etc.
(ii) The topics are, Semantic Analogy, Symbolic/Number Analogy, Figural Analogy, Semantic Classification, Symbolic/Number Classification, Figural Classification, Semantic Series, Number Series, Figural Series, Problem Solving, Word Building, Coding & de-coding, Numerical Operations, symbolic Operations, Trends, Space Orientation, Space Visualization, Venn Diagrams, Drawing inferences, Punched hole/pattern –folding & unfolding, Figural Pattern – folding and completion, Indexing, Address matching, Date & city matching, Classification of centre codes/roll numbers, Small & Capital letters/numbers coding, decoding and classification, Embedded Figures, Critical thinking, Emotional Intelligence, Social Intelligence, Other sub-topics, if any.
Important Tips
Reasoning is generally a scoring subject in comparison to the quantitative section, as it takes only thinking ability of a candidate. If the candidate is able to apply it, he can easily score well in this section. Unlike numerical skill in reasoning section you don’t have to learn some formula and solve question by applying that formula. You just have to be very careful while answering these questions. This section can’t be mastered within the given time without proper practice, so you must practice enough to score well in this section.
General Awareness
Questions in this component will be aimed at testing the candidates general awareness of the environment around him and its application to society. Questions will also be designed to test knowledge of current events and of such matters of every day observations and experience in their scientific aspect as may be expected of any educated person.
(i) The test will also include questions relating to India and its neighboring countries especially pertaining History, Culture, Geography, Economic Scene, General Policy & Scientific Research.
Important Tips
General awareness is not something you can expect to master in a day. But from an exam point of view, if you spend time consistently, you can perform well in it in relatively less time as compared to Quantitative Aptitude and Reasoning section. This section acquires more importance because this is the only section which can be attempted quickly i.e. in 12-15 minutes and at the same time, decent marks can be scored in this section if prepared well. GK also contains 25 questions of each 2 marks.
Quantitative Aptitude
The questions will be designed to test the ability of appropriate use of numbers and number sense of the candidate. The scope of the test will be computation of:-
(i) whole numbers, decimals ,fractions and relationships between numbers, Percentage. Ratio & Proportion,Square roots, Averages, Interest, Profit and Loss, Discount, Partnership Business, Mixture and Alligation, Time and distance, Time & Work.
(ii) Basic algebraic identities of School Algebra & Elementary surds, Graphs of Linear Equations, Triangle and its various kinds of centres, Congruence and similarity of triangles, Circle and its chords, tangents, angles subtended by chords of a circle, common tangents to two or more circles.
(iii) Triangle, Quadrilaterals, Regular Polygons , Circle, Right Prism, Right Circular Cone, Right Circular Cylinder, Sphere, Hemispheres, Rectangular Parallelepiped, Regular Right Pyramid with triangular or square base, Trigonometric ratio, Degree and Radian Measures, Standard Identities, Complementary angles, Heights and Distances, Histogram, Frequency polygon, Bar diagram & Pie chart
Important Tips:
The questions in this section are designed to test the ability of appropriate use of numbers and number sense of the candidates. The scope of quantitative ability is clearly defined and is limited to class 10th level mathematics. If you have good command over this section, you can score a good marks. All you need to do is attempt the questions with good accuracy. The level of this section is expected to be of moderate.
English Comprehension:
Candidates’ ability to understand correct English, his basic comprehension and writing ability, etc. would be tested. The questions in Parts A, B, & D will be of a level commensurate with the essential qualification viz. Graduation and questions in Part C will be of 10th standard level.
Important Tips: English Section is one section that gets mixed responses from candidates depending upon their educational background and preparation level. For some, this is an easy task but for others, this section becomes a nightmare and biggest hurdle in getting a good score in the exam.
I would like to say that English section is tough for those who have passed their Intermediate in Hindi Medium, but guys even I am from the same, but your Firm Decision can change things.
NOTE-1: Part C (Quantitative Aptitude) of Test booklet for Tier-I and Paper-I (Quantitative Abilities) of Tier-II will contain separate set of Questions for VH candidates only, (who have opted for assistance of scribe) which will not have components of Maps, Graphs, Statistical data, Diagram, Figures, Geometrical problems. However, components of other papers will be the same for other candidates.
NOTE-2: The Commission shall have the discretion to fix different minimum qualifying standards in each component of the Tier-I Examination taking into consideration among others, category-wise vacancies and category-wise number of candidates. Only those candidates, who have scored above the cut off marks fixed by the Commission, would be required to appear in the Tier –II Examination.
NOTE-3: Tier-I examination is used to screen the candidates for appearing in Tier-II examination for various papers which will be specifically required for different groups of posts. Marks of such screened candidates in Tier-I will be taken into account for final ranking of candidates for selecting them for the Computer Proficiency Tests/ Data Entry Skill Test and also for final selection.
Combined Graduate Level (CGL Tier-II) Pattern & Syllabus
Tier-II of the Combined Graduate Level Examination -2017 will be of Objective Type Multiple Choice and will be conducted over a period of two days.
Paper-I : Quantitative Ability:
The questions will be designed to test the ability of appropriate use of numbers and number sense of the candidate. The scope of the test will be the computation of whole numbers, decimals ,fractions and relationships between numbers, Percentage. Ratio & Proportion,Square roots, Averages, Interest, Profit and Loss, Discount, Partnership Business, Mixture and Alligation, Time and distance, Time & Work, Basic algebraic identities of School Algebra & Elementary surds, Graphs of Linear Equations, Triangle and its various kinds of centres, Congruence and similarity of triangles, Circle and its chords, tangents, angles subtended by chords of a circle, common tangents to two or more circles, Triangle, Quadrilaterals, Regular Polygons , Circle, Right Prism, Right Circular Cone, Right Circular Cylinder, Sphere, Hemispheres, Rectangular Parallelepiped, Regular Right 20 Pyramid with triangular or square base, Trigonometric ratio, Degree and Radian Measures, Standard Identities, Complementary angles, Heights and Distances, Histogram, Frequency polygon, Bar diagram & Pie chart.
Paper-II : English Language & Comprehension
Questions in this components will be designed to test the candidate’s understanding and knowledge of English Language and will be based on spot the error, fill in the blanks, synonyms, antonyms, spelling/detecting mis-spelt words, idioms & phrases, one word substitution, improvement of sentences, active/passive voice of verbs, conversion into direct/indirect narration, shuffling of sentence parts, shuffling of sentences in a passage, cloze passage & comprehension passage.
Paper-III : Statistics for Investigator Grade-II
Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation & Compiler in RGI.
Collection Classification and Presentation of Statistical Data – Primary and Secondary data, Methods of data collection; Tabulation of data; Graphs and charts; Frequency distributions; Diagrammatic presentation of frequency distributions.
Measures of Central Tendency- Common measures of central tendency – mean median and mode; Partition values- quartiles, deciles, percentiles.
Measures of Dispersion- Common measures dispersion – range, quartile deviations, mean deviation and standard deviation; Measures of relative dispersion.
Moments, Skewness and Kurtosis – Different types of moments and their relationship; meaning of skewness and kurtosis; different measures of skewness and kurtosis.
Correlation and Regression – Scatter diagram; simple correlation coefficient; simple regression lines; Spearman’s rank correlation; Measures of association of attributes; Multiple regression; Multiple and partial correlation (For three variables only).
Probability Theory – Meaning of probability; Different definitions of probability; Conditional probability; Compound probability; Independent events; Bayes’ theorem.
Random Variable and Probability Distributions – Random variable; Probability functions; Expectation and Variance of a random variable; Higher moments of a random variable; Binomial , Poisson, Normal and Exponential distributions; Joint distribution of two random variable (discrete).
Sampling Theory – Concept of population and sample; Parameter and statistic, Sampling and non-sampling errors; Probability and non-probability sampling techniques (simple random sampling, stratified sampling, multistage sampling, multiphase sampling, cluster sampling, systematic sampling, purposive sampling, convenience sampling and quota sampling); Sampling distribution(statement only); Sample size decisions.
Statistical Inference - Point estimation and interval estimation, Properties of a good estimator, Methods of estimation (Moments method, Maximum likelihood 21 method, Least squares method), Testing of hypothesis, Basic concept of testing, Small sample and large sample tests, Tests based on Z, t, Chi-square and F statistic, Confidence intervals.
Analysis of Variance - Analysis of one-way classified data and two-way classified data. Time Series Analysis - Components of time series, Determinations of trend component by different methods, Measurement of seasonal variation by different methods.
Index Numbers - Meaning of Index Numbers, Problems in the construction of index numbers, Types of index number, Different formulae, Base shifting and splicing of index numbers, Cost of living Index Numbers, Uses of Index Numbers.
Paper IV:
General Studies (Finance and Economics) for the post of Assistant Audit Officer in Indian Audit & Accounts Department under CAG.
Part A: Finance and Accounts-(80 marks)
- Fundamental principles and basic concept of Accounting. Financial Accounting: Nature and scope, Limitations of Financial Accounting, Basic concepts and Conventions, Generally Accepted Accounting Principles. Basic concepts of accounting: Single and double entry, Books of original Entry, Bank Reconciliation, Journal, ledgers, Trial Balance, Rectification of Errors, Manufacturing, Trading, Profit & loss Appropriation Accounts, Balance Sheet Distinction between Capital and Revenue Expenditure, Depreciation Accounting, Valuation of Inventories, Non-profit organisations Accounts, Receipts and Payments and Income & Expenditure Accounts, Bills of Exchange, Self Balancing Ledgers.
Part B: Economics and Governance-(120 marks)
- Comptroller & Auditor General of India- Constitutional provisions, Role and responsibility
- Finance Commission-Role and functions
- Basic Concept of Economics and introduction to Micro Economics
- Theory of Demand and Supply Meaning and determinants of demand, Law of demand and Elasticity of demand, Price, income and cross elasticity; Theory of consumer’s behaviour-Marshallian approach and Indifference curve approach, Meaning and determinants of supply, Law of supply and Elasticity of Supply.
- Theory of Production and cost Meaning and Factors of production; Laws of production- Law of variable proportions 22 and Laws of returns to scale. 7. Forms of Market and price determination in different markets Various forms of markets-Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly ad Price determination in these markets
- Indian Economy Nature of the Indian Economy Role of different sectors-Role of Agriculture, Industry and Services-their problems and growth; National Income of India-Concepts of national income, Different methods of measuring national income Population-Its size, rate of growth and its implication on economic growth Poverty and unemployment- Absolute and relative poverty, types, causes and incidence of unemployment Infrastructure-Energy, Transportation, Communication
- Economic Reforms in India: Economic reforms sice 1991; Liberalisation, Privatisation, Globalisation and Disinvestment
- Money and Banking Monetary/ Fiscal policy- Role and functions of Reserve Bank of India; functions of commercial Banks/RRB/Payment Banks Budget and Fiscal deficits and Balance of payments Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003 11. Role of Information Technology in Governance
Few Important Points to be remember:
(i): Paper-I & II are compulsory for all the categories of posts.
(ii): Paper-III is only for those candidates who apply for the post of Statistical Investigator Gr.II & Compiler.
(iii): Paper IV is only for those candidates who apply for the post of Assistant Audit Officer.
(iv): Candidates opting for the post of Compiler and/or Statistical Investigator Gr. II and Assistant Audit Officer must ensure that they possess the requisite qualification as mentioned above. Commission reserves the right to take appropriate action against applicants who do not possess the requisite eligibility while opting for the post of Compiler and/or Statistical Investigator Gr. II and Assistant Audit Officer.
SSC CGL Exam is expected to be held in the month of May, 2017. Also this year, the number of applicants are expected to be higher with slightly lower vacancies as compared to last year.

No comments:
Post a Comment
Thank You